The SQL format
Sometimes referred to as an “SQL Dump”, SQL files are a text based format. An SQL file is a list of SQL commands that create and fill the tables in a database system. A dump for an example table could look like this:
| Example Table: |
|
|||||||||
| SQL Dump: |
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS phones; CREATE TABLE phones(ID INT, Name TEXT, Thickness FLOAT); INSERT INTO phones(ID,Name,Thickness) VALUES(1,'iPhone 3GS',12.3); INSERT INTO phones(ID,Name,Thickness) VALUES(2,'iPhone 4',9.3); |
As you can see from the example, an SQL dump consists of three kinds of statements:
-
DROP TABLE
Before we can create a new table, we must first delete any existing table with the same name. -
CREATE TABLE
This command creates a new table on the database server. It specifies the structure, defining field names and types. There is one CREATE TABLE command for every table in the SQL dump file. -
INSERT
These statements fill the tables with content. There is one INSERT statement for every row in the table.
When exporting to SQL, you can choose not to include the CREATE TABLE statements. This is useful when you already have the necessary table structure on the server. The SQL file will then only contain the data inside the tables. If you choose this option, you must ensure that the tables on the server have the same field names as the tables in the Access database.
Similarly, if you want to export only the table structure, you can choose to not export the data (INSERT statements).
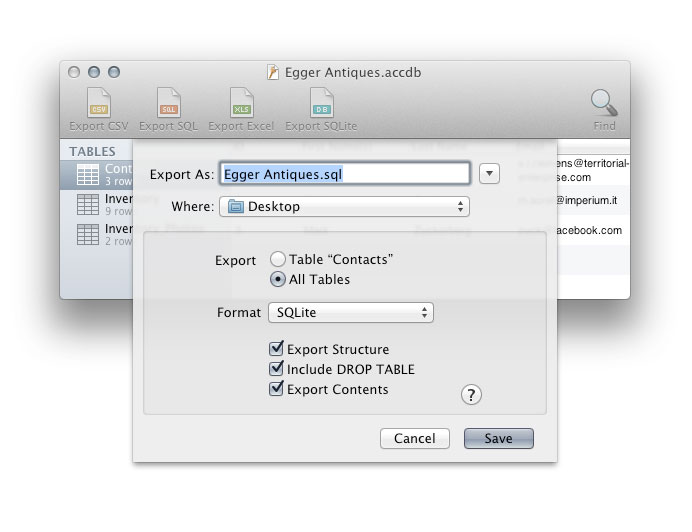
An SQL file can contain multiple tables. It is therfore very convenient for storing entire databases.
Database-specific instructions
Since the SQL language is not consistent among different database systems, MDB Viewer allows to export SQL dumps in different “flavors”. See the following sections for database-specific information: